Investment Thesis
As the competition among manufacturers of electric vehicles (EV) heats up globally, Tesla, Inc. (NASDAQ:TSLA) has reduced prices for certain of its Model Y and Model 3 vehicles in the U.S. for the sixth time this year in an effort to boost demand. Despite the strong pullback in Tesla stock, TSLA remains a strong contributor to the Yiazou model portfolio, and considering the improving outlook, the strong buy rating is reaffirmed for the medium term.
Sacrificing Margins For Volume: Post-Q1 Outlook
In an unusual pattern, Tesla’s profit and free cash flow declined sharply in the first quarter of 2023 due to the impact of notable price cuts. The company slashed prices in the quarter. This was done to allow some models to qualify for federal purchase credits under the Inflation Reduction Act in the U.S., but mostly to stimulate demand as people may be less inclined to buy, for instance, due to rising borrowing costs. Further price cuts were implemented in April, and the leadership does not rule out making even further cuts.
The improved affordability of Tesla cars has helped Tesla to show accelerated delivery growth again. Tesla’s priority is to grow its car fleet further as economies have weakened and competition is heating up. The firm expects its margins to remain among the highest in the car industry but is willing to suffer considerable pressure in the near term to spur car volume growth. It defends this strategy by arguing that it has much better possibilities than rivals to earn additional profits from its customer base after the initial sale. In addition, it aims to capture services and software income, mostly related to the usage of its self-driving system, which the leadership believes could become a meaningful profit driver over time.
Data by YCharts
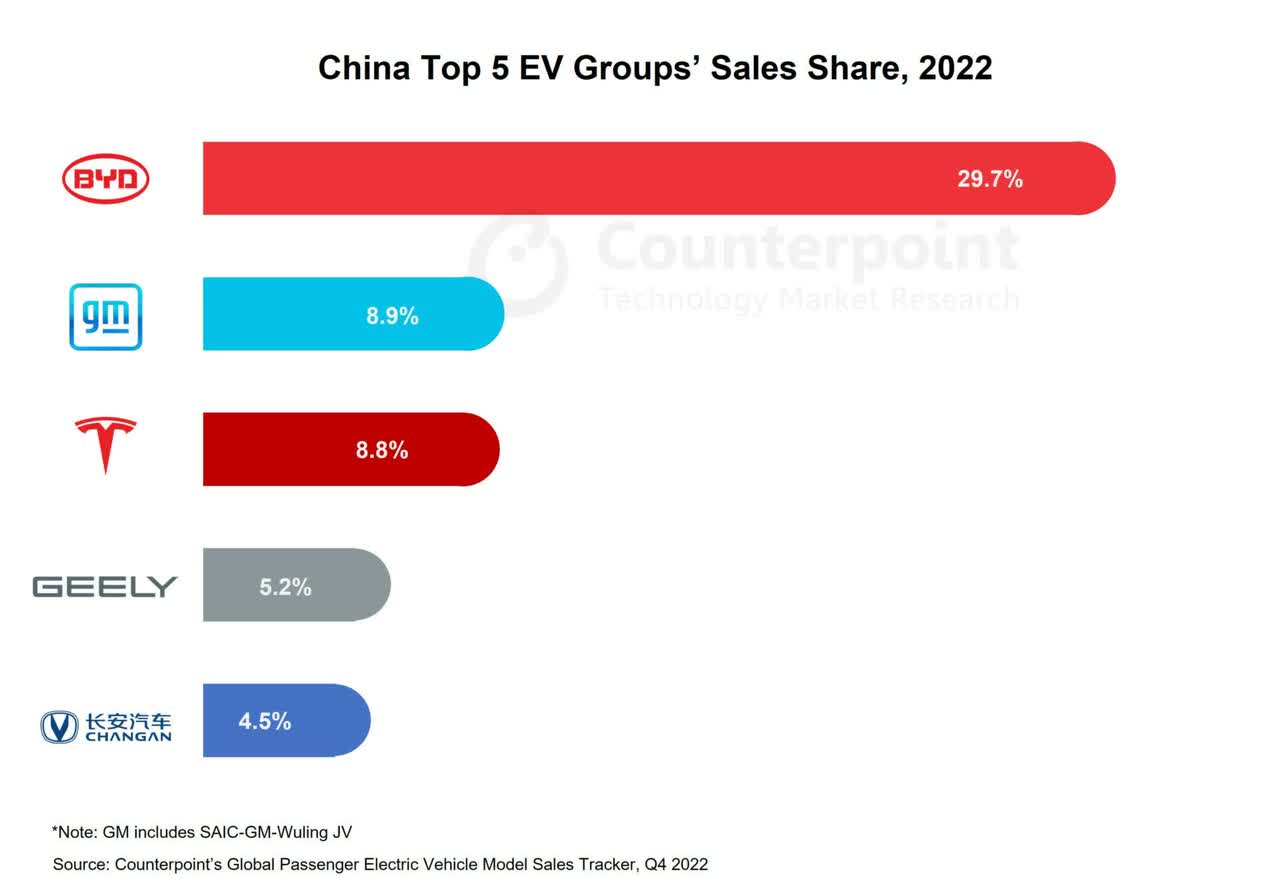
The company is well positioned to gain further share, helped by the structural transition from internal combustion engine (ICE) cars to models with a lower environmental impact. This shift is likely accelerating, with help from global government initiatives and the category’s rising competitiveness. However, impacted by rising competition, Tesla has lost some ground in the all-electric category in recent years, especially in recent quarters with notable losses in China, due to the success of local vendors, China’s leading car firm BYD Company Limited (OTCPK:BYDDF, OTCPK:BYDDY) in particular.
Tesla will also continue to enjoy important competitive benefits against legacy carmakers and new electric car specialists. The company benefits from a fast-rising scale, which is crucial to operating in a cost-efficient way, and similar to BYD, Tesla’s business model enjoys a high level of vertical integration. Tesla primarily uses its software, designs its chips, and many key car components. A few years ago, Tesla started to work on in-house production of its battery cells, which should complement batteries made by strategic partner Panasonic and sourced from leading makers such as Chinese firm CATL. The strategy should reduce the risks of shortages and help Tesla grow its competitive advantage in the long term.
Additional Price Cuts To Unlock More Volume
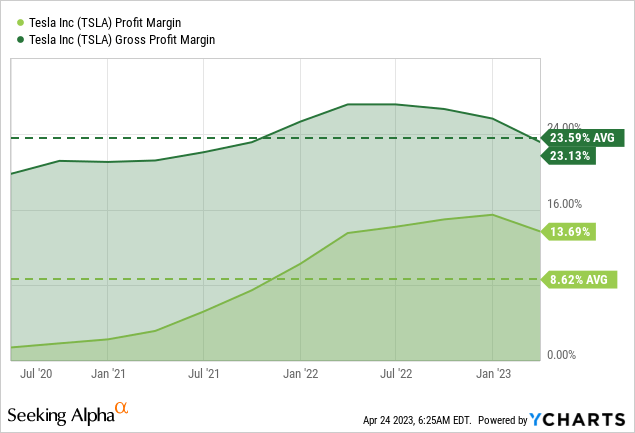
Tesla’s decision to cut prices is causing concern among investors, who fear it may negatively impact the company’s margins. However, Tesla has assured its shareholders that its gross margins will not fall below 20% in any quarter of 2023 and that the first quarter of the year will be the low point. Nevertheless, reducing prices is expected to be a crucial part of Tesla’s strategy to increase sales, particularly as it expands production capacity.
Tesla’s strategy involves using its cost advantage to finance growth in volume. While price cuts may be a problem for Tesla, they are even more problematic for other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), who are at a clear margin/cost disadvantage compared to Tesla. Tesla’s margins are higher than those of ICE margins of other OEMs, and EV margins for legacy OEMs are still largely negative. Given that other OEMs will likely take a long time to achieve appropriate EV margins, Tesla’s cost advantage is expected to be sustained for some time.
Investors closely monitor various demand indicators, such as weekly registration data, delivery wait times, and inventory levels, which will remain a key focus throughout the year until more details about the next-gen platform are released. In the short term, Tesla’s “Highland” project, aimed at reducing costs and boosting demand by refreshing the five-year-old Model 3, could help with demand and margin but may require extended factory downtime that could hurt volumes.
However, the redesigned vehicle is expected to include an updated exterior and powertrain performance and will likely begin production in Shanghai soon and in Fremont later this year. In addition, Tesla is also reportedly planning a new Model Y revamp under a project called “Juniper.” Ultimately, these refreshes of Tesla’s top models will help the company remain competitive, particularly in the rapidly growing Chinese EV market. As a result, many new entrants are entering the Model 3/Y segments and taking back market share.
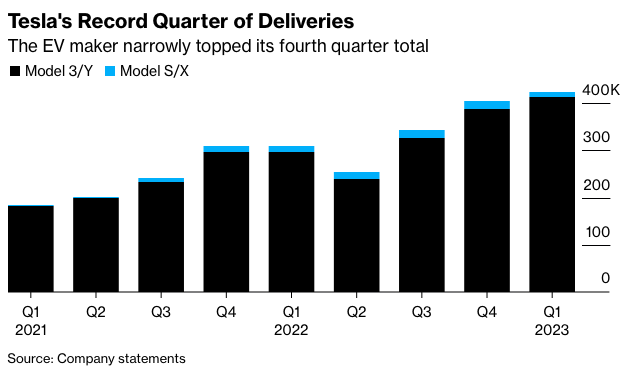
Bloomberg
Next-Gen Platform Remains A Catalyst In 2024
Tesla’s next-gen platform will cut costs significantly, as the cost structure of the next-gen platform does not solely depend on the company’s ability to achieve maximum battery cost reductions. In addition, the vehicle design, architecture, and manufacturing efficiencies will also contribute to reducing costs.
Additionally, improvements in batteries and powertrain will further reduce the cost of the next-gen platform by 50% compared to current Model 3/Y products. Although financial details were not disclosed, the company has shared some insights into its technology and manufacturing advancements that support its cost leadership and ability to increase volume while reducing costs. This aligns with its goal to produce 20 million vehicles as part of a sustainable future.
If Tesla succeeds in these initiatives, it will strengthen its competitive position in the electric vehicle market for many years, despite needing more visibility on its project roadmap in the short to medium term. With the confirmed location of its Mexico facility, the company aims to start production in late 2024 or early 2025, following the rapid construction timeline of its Shanghai facility.
Tesla Faces Intense Competition In China
Tesla has shown signs of regaining market share from BYD, which recently announced plans to reduce output for some key EV programs, possibly due to demand shifts following Tesla’s price cuts. In addition, industry groups in China have called for a slowdown in the pricing war, citing financial challenges for OEMs. While this situation may impact Tesla’s margins, the company will likely have better cushioning against these challenges than competitors due to its mature supply chains, efficient operations, and strong brand positioning that allows it to sell based on brand value rather than price.
BYD has, in the past decade, clearly benefited from the policies of the Chinese government, which wants the country to become a global leader in both batteries and electric cars. As a result, BYD stepped up its efforts to start exports to Europe last year and expects to sell over 3 million cars this year. This represents 66% growth, well ahead of Tesla’s target of 38%. Nevertheless, Tesla is still substantially more profitable than BYD, whose cars are much lower-priced.
Despite lower selling prices, the Chinese rival has still improved its margin, and the gains may continue, thanks to rising efficiencies from scale and some key advantages. These include BYD’s leading position in China, the world’s largest car market, and significant control over key inputs. BYD started as a battery producer and is among the world’s three largest battery makers. BYD also makes its own chips and will continue to benefit from relatively low operating costs in China compared to other markets, as well as from the ample supply of minerals in China and the country’s lead in processing key battery materials such as cobalt and lithium.
Counterpoint
Takeaway
Despite the supply chain and other short-term challenges that put significant pressure on Tesla, Inc., the worst appears over. The EV industry is expected to normalize in the year’s second half, exposing TSLA stock to the additional upside. Nevertheless, the trend toward electrification of transportation is unavoidable, and following the pullback, Tesla, Inc. provides another reasonable entry point to capitalize on this trend.
Editor’s Note: This article discusses one or more securities that do not trade on a major U.S. exchange. Please be aware of the risks associated with these stocks.
Author of Yiazou Capital Research
This article was written by